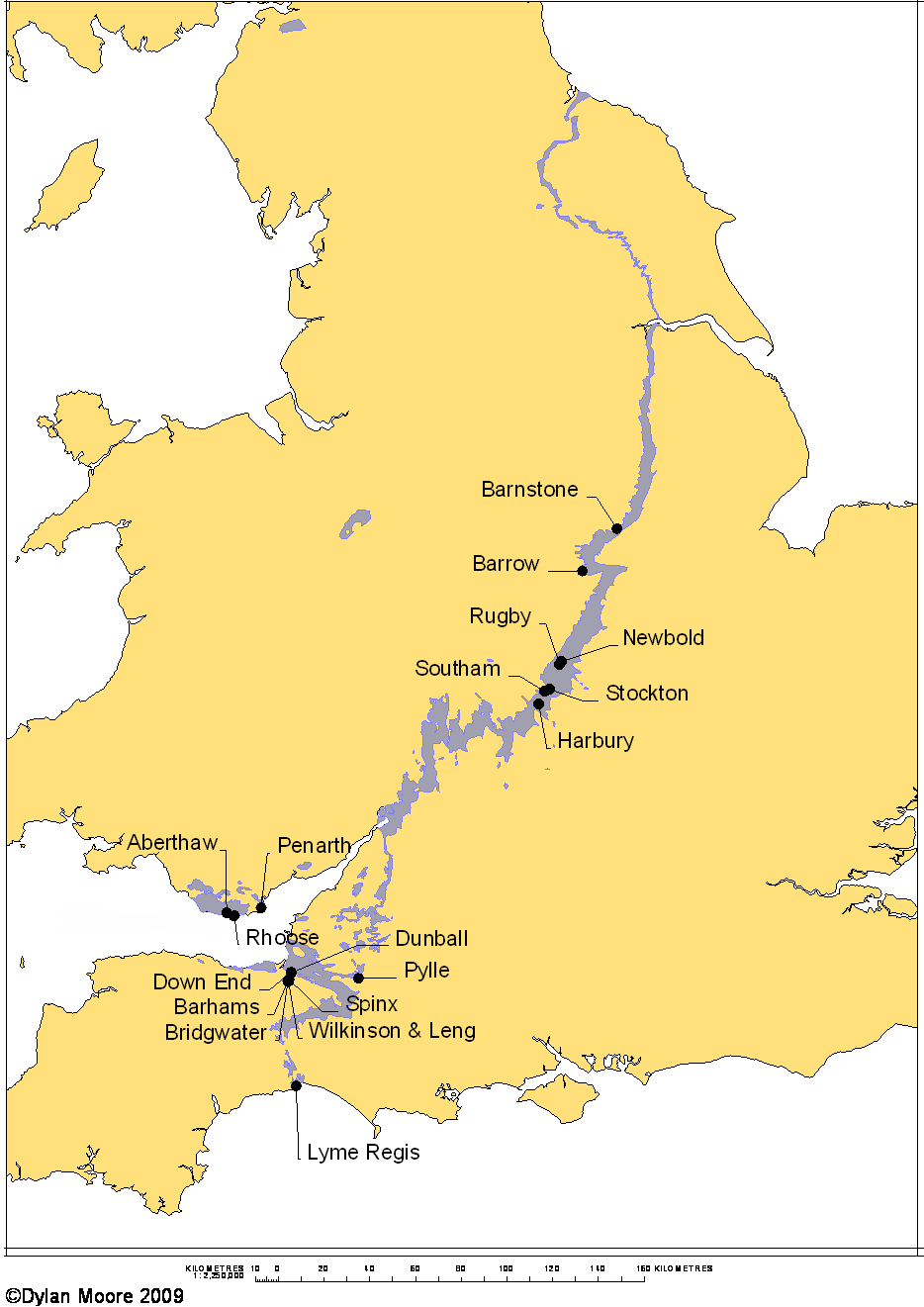
 The plant names on this map are clickable unless resized by device.
The plant names on this map are clickable unless resized by device.
Although it is a Jurassic Limestone, this formation deserves to be treated separately, because of its unique chemistry and because of the large number of plants that have exploited its special properties. It lies at the base of the Jurassic, where often the junction with the Triassic is conformable, and at many locations the bottom few layers identified as Lias are in fact in the Triassic, while the underlying "White Lias" stone is always Triassic. It consists of alternating bands of argillaceous limestone and calcareous clay or shale, typically each a few inches thick and blue/grey in colour. Many quarries have over 50 layers. Foe detailed geology, see below. The Blue Lias has outcrops stretching across the middle of England from the Dorset coast to the Cleveland Hills in Yorkshire. It also forms much of the Vale of Glamorgan, and there is a small outlier in the Cheshire Basin. It occurs under the Irish Sea. The blue colour of both rocks derives from pyrite, and both oxidise to orange-brown on exposure to air.
The limestone, historically separated by hand by pick and bar, has been used for centuries for building blocks, paving slabs, and for the preparation of hydraulic limes, many of which had the qualities of natural cement. During the late 18th and 19th centuries, improved communications allowed Lias limes to be widely distributed. In particular, the canal systems allowed Warwickshire lime to be distributed throughout the industrial Midlands and to London. The Blue Lias lime gained a country-wide reputation for its hydraulicity and was much used for stucco, and as an engineering cement in the pre-Portland period. When John Smeaton made his famous experiments on hydraulicity in connection with his Eddystone lighthouse project, the hydraulic limes he finally chose to use were both from the Blue Lias; from Watchet, Somerset and Aberthaw, Glamorgan, on opposite sides of the Bristol Channel. Because of this already-established trade, after Portland cement was invented, a number of Lias-based manufacturers claimed to make it, simply by burning the stone a little harder, and it is often difficult to tell when they started to make a “true” Portland product containing alite.
In view of the fact that Blue Lias lime already had wide use in the building industry, it is not unnatural that when Portland cement started to gain a good reputation in the 1860s, Blue Lias lime manufacturers tried to make it. Over-confidence in the excellence of their stone led them initially to try making it by burning the as-dug rock just as they did for lime, only a little hotter. However, the variability, both layer-to-layer and laterally, of the limestone was too great to make an acceptable product by this method.
Henry Reid (p 168) said “Before and during the year 1868, the author in common with most engineers looked upon “Portland cement" from Warwickshire and Somersetshire . . . with much suspicion, and generally characterized it as worthless and false. Its sale was limited and confined to small consumers, to whom its best recommendation was cheapness, and within so circumscribed a limit of intelligence the damage sustained was not of a very serious character.”
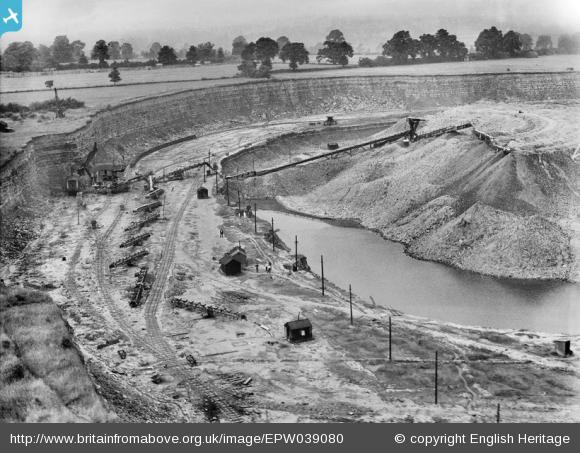 Picture: ©Historic England - NMR Aerofilms Collection. Britain from Above reference number EPW039080.
Picture: ©Historic England - NMR Aerofilms Collection. Britain from Above reference number EPW039080.Britain from Above features some of the oldest and most valuable images of the Aerofilms Collection, a unique and important archive of aerial photographs. You can download images, share memories, and add information. By the end of the project in 2014, 95,000 images taken between 1919 and 1953 will be available online.
Southam quarry in July 1932. The Lias was blasted and transferred by face shovel to a mobile screener. The coarse limestone was transferred to the plant by tramway, and the fine shale was mostly side-cast in the worked out part of the quarry by a system of conveyors.
Operators extracted the identifiable layers individually, and became familiar with their chemical properties, and at each location, the seams were given identifying names. These names are listed and discussed at length in a separate article.
Real Portland cement finally began to be made by fine-grinding and blending the limestone, making judicious use of the known high- and low-grade layers to adjust the mix. The earliest seems to have been Harbury (1864). It is interesting to note that cement plants grew only where there was a pre-existing lime industry, and in other parts of the outcrop where lime was not produced – because of alternative sources of lime – a cement industry never developed.
Scale-up of output of the Lias plants meant that the traditional hand-picking of the stone was no longer economically viable. The initial solution to the problem was to dig or blast the rock en masse and then to roughly separate the harder limestone from the softer clay by means of a “rumbler” – a rotating cylinder of iron bars through which the mixture was rolled. The crumbled clay fell through the bars and the large chunks of limestone emerged at the end. With this method, chemical control now relied on blending material with known larger or smaller proportions of high-grade stone.
The separation of the components is seen in the picture to the right. The regular variations in the Lias are believed to be Milankovitch cyclothems, which means that they result from regular variations of climate on a global scale, so individual identifiable layers can be traced over long distances. On the other hand, the chemistry of the layers, and the relative amounts of limestone and shale, are very sensitive to local deposition conditions. Generally the richest lias has around 85% limestone by mass, whereas in some locations it may disappear altogether. The deposit shown contained about 32% limestone.
Generally, the separated limestone mixture was of marginal chemistry (i.e. around 75-80% CaCO3) with little scope for adjustment. As the requirement for higher calcium contents evolved during the 20th century, Lias plants mostly started bringing in high-grade limestone from elsewhere to “sweeten” the mix. This was sourced from the Rhaetic (below the Lias), the Inferior Oolite and Great Oolite (above it), the Carboniferous Limestone or even from the very distant Chalk. Having arranged this, raw material preparation costs were reduced further by using the whole of the Blue Lias, un-separated. The evolution of mix design can be seen in the raw material usage data of the Stockton plant:
| Period | Lias Stone % | Lias Clay % | Oolite % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1880-89 | 92.9 | 7.1 | 0.0 |
| 1890-99 | 93.4 | 6.6 | 0.0 |
| 1900-09 | 93.8 | 6.2 | 0.0 |
| 1910-18 | 97.8 | 2.2 | 0.0 |
| 1919-24 | 89.7 | 3.0 | 7.3 |
| 1925-30 | 88.5 | 3.1 | 8.4 |
| 1931-36 | 95.4 | 1.2 | 3.4 |
| 1937-45 | 86.0 | 3.5 | 10.5 |
Many plants remained small with static kilns, yet managed to hang on until the middle of the 20th century. The larger plants installed rotary kilns. All but one opted for use of the Wet Process although dry processing is easily effected. The exception was Southam, and the dry process kilns there were soon converted to wet process. After a long wait, Aberthaw converted to dry process from 1967, and two kilns were converted to semi-wet operation at Southam from 1978. Rugby was converted to a mixed dry and wet process precalciner in 2002. With the closure of Southam in 2000, the only remaining plants are Aberthaw and Rugby (the latter now predominantly using chalk as a raw material).
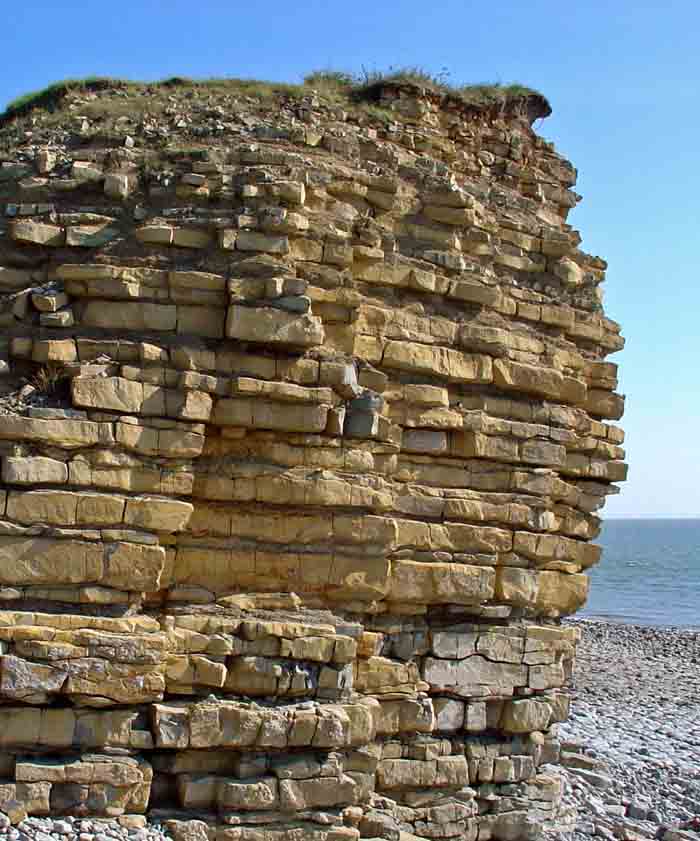

Blue Lias at Rhoose. The deposit here contains about 69% limestone, the carbonate content of which is 75-80%.
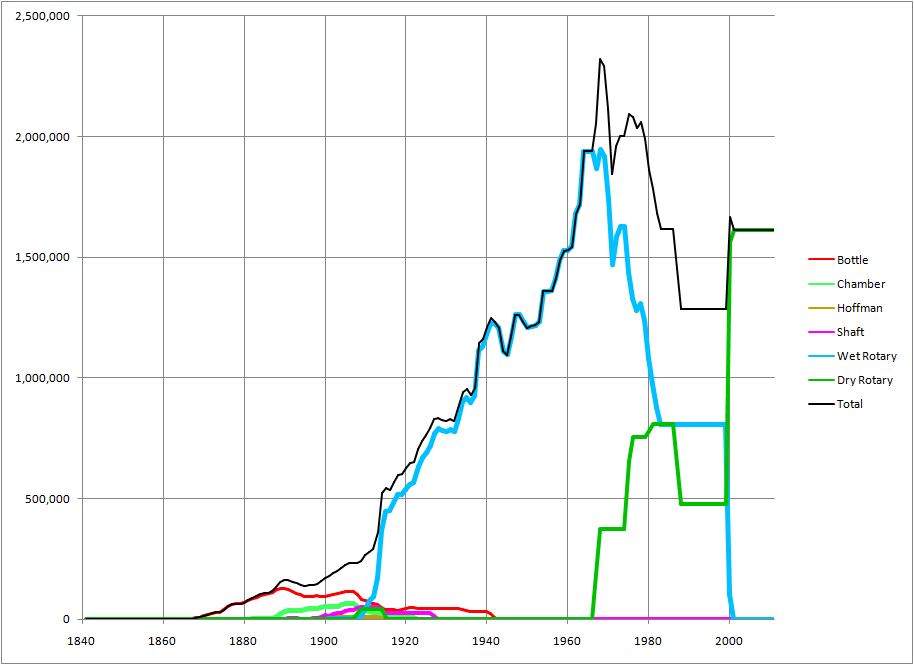
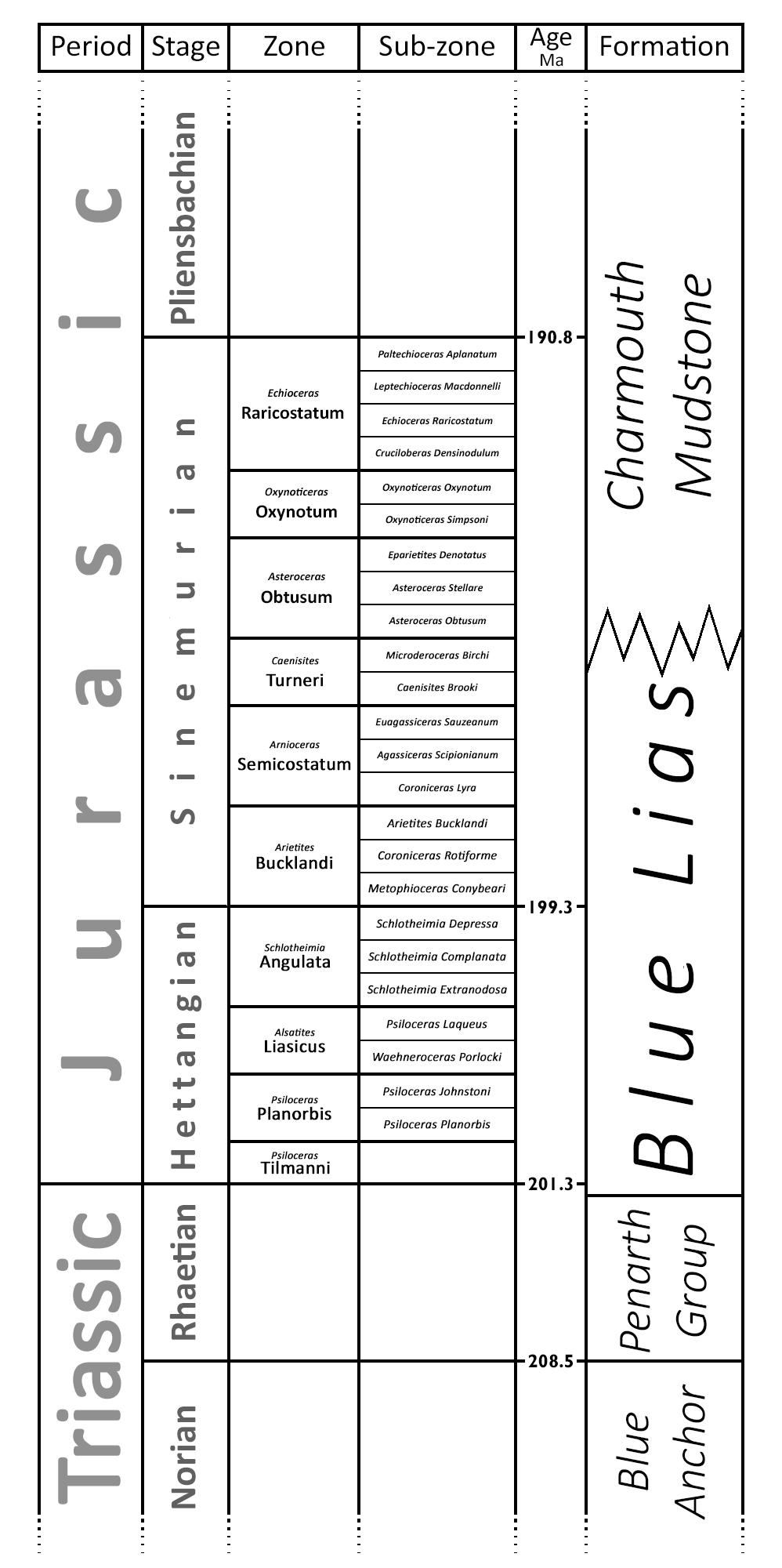 Chart showing relation of the "Blue Lias" to its neighbouring formations, and to the chronostratigraphic column. Age not to scale.
Chart showing relation of the "Blue Lias" to its neighbouring formations, and to the chronostratigraphic column. Age not to scale.
Stratigraphy
The Blue Lias stratigraphically spans the Rhaetian, Hettangian and Sinemurian stages. The top and bottom of the formation are defined in terms of lithology - specifically sharp changes in limestone/shale ratio - so they are subject to local conditions and do not correspond exactly with stratigraphic zone boundaries. The bottom boundary in particular has been contentious, since the Triassic/Jurassic boundary lies close to it, but perhaps slightly above. The base of the Jurassic is formally defined as the point of arrival of Psiloceras ammonites, which appeared to be lacking in the first few metres of the Blue Lias, but subsequent discoveries have claimed most of this for the Jurassic. The top boundary is even more vague, since the overlying Charmouth Mudstones are often quite similar to Blue lias.
In many areas, large parts of the succession are missing, and the boundaries may vary because of this. The ratio of limestone to shale is also very variable laterally, and limestones often disappear over large parts of the formation. North of Leicester on the outcrop, the lithology of the upper part changes, and it has been re-named the Scunthorpe Mudstone Formation. The underlying Penarth Group (historically called the Rhaetic) and the overlying Charmouth Mudstones, on the other hand, continue throughout the length of the outcrop.
The diagram to the right shows how the Blue Lias and its neighbours fit into the international stratigraphic classifications. It can be seen that the Blue Lias occupies all of the Hettangian, and the lower part of the Sinemurian. Correlation with individual zones and sub-zones varies locally and must be seen alongside the subdivision of the formation into localised "members", best discussed in terms of the various regions in which the rock was used.
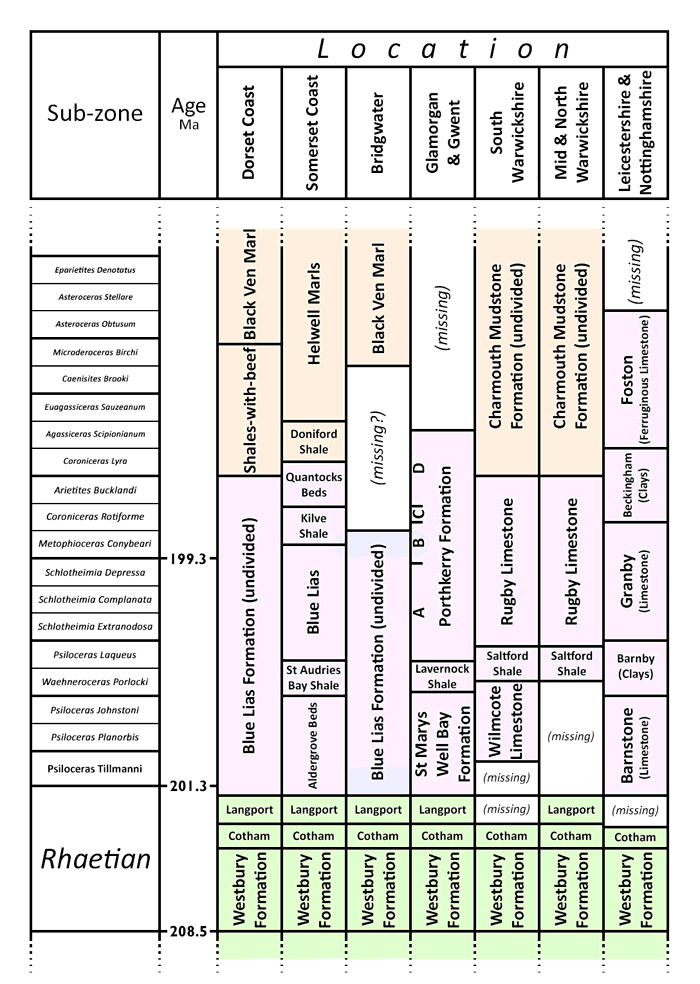 Chart showing local members of the Blue Lias and its neighbouring formations. Age not to scale.
Chart showing local members of the Blue Lias and its neighbouring formations. Age not to scale.
Local Members
The BGS official designation of the Blue Lias Formation (or Scunthorpe Mudstone Formation north of Leicester) is rather loosely defined in terms of lithology. The base is a (usually) sharp non-sequence boundary with the Rhaetic. The overlying Charmouth Mudstone Formation contains similar limestones and shales, and the boundary is defined by a consistent step-change reduction in the limestone/shale ratio - ultimately requiring a statistical analysis to judge objectively.
The limestone/shale ratio also changes within the formation sufficiently consistently to suggest division into named members, defined solely by this ratio. In particular, a layer with comparatively sparse limestone occurs in the Liasicus zone. This manifests itself as the informal St Audries Bay Shale in coastal Somerset, the Lavernock Shale Member in Glamorgan and Gwent, the Saltford Shale Member in the south Midlands, and the Barnby Member north of Leicester. The Blue Lias is not officially divided at Lyme Regis, but the same trend is visible in a 1.8 m section (Lang layers H67-H71). Although all but the lowest part of the Blue Lias is buried under the Somerset Levels in the Bridgwater area, a borehole at Brent Knoll to the east shows the same patterns of limestone-rich and limestone-poor shales as in the coastal section, so a shale member in the Liassicus zone is a universal feature. This interruption divides the formation in most places into an upper and lower member, as shown in the table.
The location of individual cement plant quarries in the stratigraphic column is tabulated as follows.
| plant | member | sub-zones |
|---|---|---|
| Lyme Regis | Blue Lias | Complanata-Bucklandi |
| Bridgwater | Aldergrove | Tillmanni-Planorbis |
| Pylle | Quantocks | Rotiforme-Bucklandi |
| Aberthaw | Porthkerry | Depressa-Bucklandi |
| Rhoose | Porthkerry | Complanata-Rotiforme |
| Penarth | St Marys Well Bay | Tillmanni-Porlocki |
| Harbury | Rugby Limestone | Depressa-Bucklandi |
| Southam* | Rugby Limestone | Laqueus-Bucklandi |
| Barrow | Barnstone | Tillmanni-Porlocki |
| Barnstone | Barnstone | Tillmanni-Johnsoni |
Note: *Stockton, Rugby and Newbold are similar to Southam.